在之前的博文《SystemTap Kprobe原理》中简要的对kprobe进行了介绍,Kprobe机制是内核提供的一种调试机制,它提供了一种方法,能够在不修改现有代码的基础上,灵活的跟踪内核函数的执行。
kprobe工作原理是:
1)在注册探测点的时候,将被探测函数的指令码替换为int 3的断点指令;
2)在执行int 3的异常执行中,CPU寄存器的内容会被保存,通过通知链的方式调用kprobe的异常处理函数;
3)在kprobe的异常处理函数中,首先判断是否存在pre_handler钩子,存在钩子则执行pre_handler;
4)进入单步调试,通过设置EFLAGS中的TF标志位,并且把异常返回的地址修改为保存的原指令码;
5)代码返回,执行原有指令,执行结束后触发单步异常;
6)在单步异常的处理中,清除标志位,执行post_handler流程,并最终返回执行正常流程;
Kprobe提供了三种形式的探测点,一种是最基本的kprobe,能够在指定代码执行前、执行后进行探测,但此时不能访问被探测函数内的相关变量信息;一种是jprobe,用于探测某一函数的入口,并且能够访问对应的函数参数;一种是kretprobe,用于完成指定函数返回值的探测功能。而jprobe与kretprobe都是基于kprobe实现的。
下面对kprobe代码简要分析:
在init_kprobes()初始化函数中,将kprobe注册到kprobe_exceptions_notify通知链
static int __init init_kprobes(void)
{
...
err = arch_init_kprobes();
if (!err)
err = register_die_notifier(&kprobe_exceptions_nb);
if (!err)
err = register_module_notifier(&kprobe_module_nb);
kprobes_initialized = (err == 0);
if (!err)
init_test_probes();
return err;
}
static struct notifier_block kprobe_exceptions_nb = {
.notifier_call = kprobe_exceptions_notify,
.priority = 0x7fffffff /* we need to be notified first */
};
int __kprobes register_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)函数则是我们在内核模块中所调用的,经过对调用点一系列的检查,最后将将kprobe加入到相应的hash表内,并将将探测点的指令码修改为int 3指令: __arm_kprobe(p);
int __kprobes register_kprobe(struct kprobe *p) {
...
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&p->hlist);
hlist_add_head_rcu(&p->hlist,
&kprobe_table[hash_ptr(p->addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)]);
if (!kprobes_all_disarmed && !kprobe_disabled(p))
__arm_kprobe(p);
...
当内核调用到这个探测点时,触发int 3,经过中断处理,调用到do_int3() 函数,如果我们使能了CONFIG_KPROBES选项,那么跳入kprobe_int3_handler执行,该函数为kprobe的核心函数。
dotraplinkage void notrace do_int3(struct pt_regs *regs, long error_code)
{
...
#ifdef CONFIG_KPROBES
if (kprobe_int3_handler(regs))
goto exit;
#endif
if (notify_die(DIE_INT3, "int3", regs, error_code, X86_TRAP_BP,
SIGTRAP) == NOTIFY_STOP)
goto exit;
...
exit:
ist_exit(regs);
}
static int __kprobes kprobe_handler(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
...
addr = (kprobe_opcode_t *)(regs->ip - sizeof(kprobe_opcode_t));
//对于int 3中断,那么异常发生时EIP寄存器内指向的为异常指令的后一条指令
preempt_disable();
kcb = get_kprobe_ctlblk();
/*获取addr对应的kprobe*/
p = get_kprobe(addr);
if (p) {
//如果异常的进入是由kprobe导致,则进入reenter_kprobe
if (kprobe_running()) {
if (reenter_kprobe(p, regs, kcb))
return 1;
} else {
set_current_kprobe(p, regs, kcb);
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_ACTIVE;
/*
* If we have no pre-handler or it returned 0, we
* continue with normal processing. If we have a
* pre-handler and it returned non-zero, it prepped
* for calling the break_handler below on re-entry
* for jprobe processing, so get out doing nothing
* more here.
*/
//执行在此地址上挂载的pre_handle函数
if (!p->pre_handler || !p->pre_handler(p, regs))
//设置单步调试模式,为post_handle函数的执行做准备
setup_singlestep(p, regs, kcb, 0);
return 1;
}
} else if (*addr != BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION) {
...
} else if (kprobe_running()) {
...
} /* else: not a kprobe fault; let the kernel handle it */
preempt_enable_no_resched();
return 0;
}
setup_singlestep() 函数为单步调试函数,在该函数内会打开EFLAGS的TF标志位,清除IF标志位(禁止中断),并设置异常返回的指令为保存的被探测点的指令。
static void __kprobes setup_singlestep(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs,
struct kprobe_ctlblk *kcb, int reenter)
{
if (setup_detour_execution(p, regs, reenter))
return;
...
/*jprobe*/
if (reenter) {
save_previous_kprobe(kcb);
set_current_kprobe(p, regs, kcb);
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_REENTER;
} else
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_SS;
/* Prepare real single stepping */
/*准备单步模式,设置EFLAGS的TF标志位,清除IF标志位(禁止中断)*/
clear_btf();
regs->flags |= X86_EFLAGS_TF;
regs->flags &= ~X86_EFLAGS_IF;
/* single step inline if the instruction is an int3 */
if (p->opcode == BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION)
regs->ip = (unsigned long)p->addr;
else
/*设置异常返回的指令为保存的被探测点的指令*/
regs->ip = (unsigned long)p->ainsn.insn;
}
setup_singlestep() 执行完毕后,程序继续执行保存的被探测点的指令,由于开启了单步调试模式,执行完指令后会继续触发异常,这次的是do_debug异常处理流程。然后在kprobe_debug_handler恢复现场,清除TF标志位等操作,完成kprobe调用。
dotraplinkage void do_debug(struct pt_regs *regs, long error_code)
{
...
#ifdef CONFIG_KPROBES
if (kprobe_debug_handler(regs))
goto exit;
#endif
...
}
int kprobe_debug_handler(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
...
resume_execution(cur, regs, kcb);
regs->flags |= kcb->kprobe_saved_flags;
if ((kcb->kprobe_status != KPROBE_REENTER) && cur->post_handler) {
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_SSDONE;
cur->post_handler(cur, regs, 0);
}
/* Restore back the original saved kprobes variables and continue. */
if (kcb->kprobe_status == KPROBE_REENTER) {
restore_previous_kprobe(kcb);
goto out;
}
reset_current_kprobe();
...
}
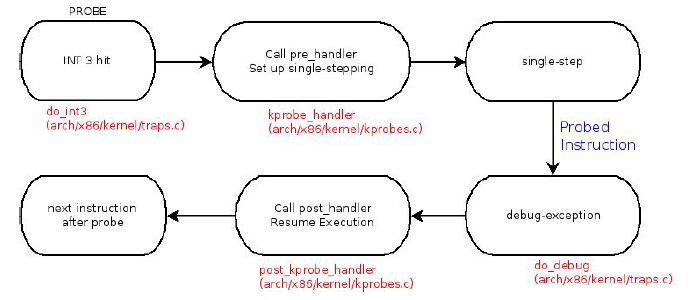
总结一下kprobe流程就是下图:
参考:
https://lwn.net/Articles/132196/
http://www.lxway.com/82244406.htm
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-22227409-id-3420260.html