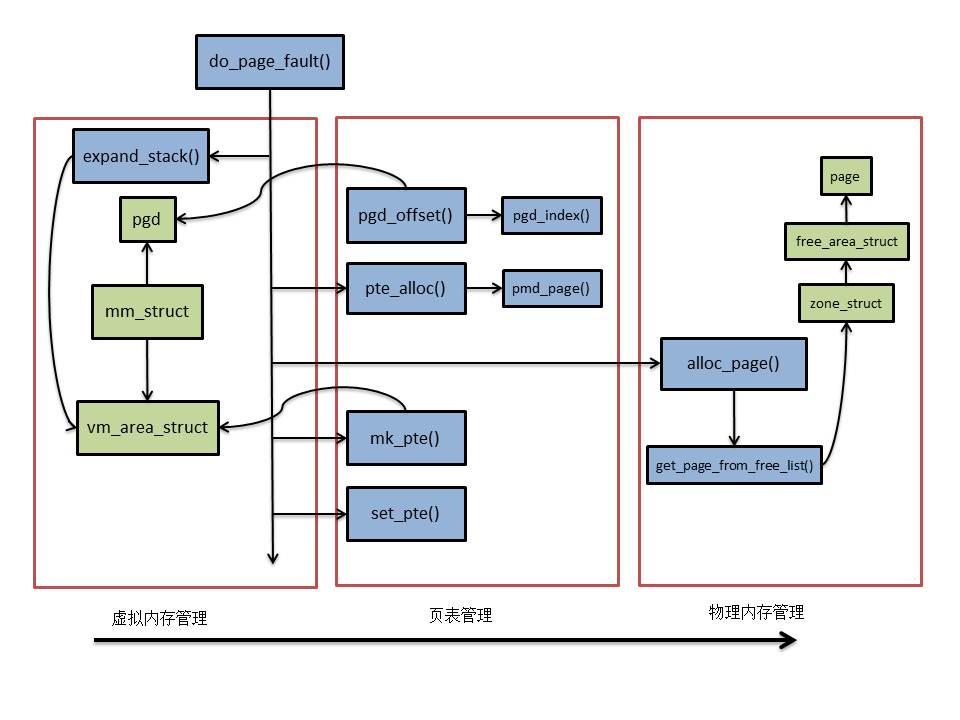
通过打印VFS结构体,我们可以快速掌握VFS主要结构体之间的关系
详见http://www.lizhaozhong.info/archives/1080
我之前在网上找了许多资料,都是关于linux 2.X的,有个问题在与inode中的i_dentry在linux 3.X中以hlist形式出现,我们都知道hash list比其一般的list_head查找速度更快。尤其是在大规模的链表中,具体的hlist定义在include/linux/list.h中。
他们都是一个个宏函数:
#define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member)
#define hlist_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos ; pos = pos->next)
#define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }); \
pos = n)
.......
用法与list差不多http://www.lizhaozhong.info/archives/951
这里就不一一说明了。
我们要知道从super_block到inode,然后从inode寻找dentry是可行的。inode与dentry本来就是互通的。
包括从task_struct指向struct file -> dentry->inode都是可行的,比较灵活.
这里要说明的是前面那4个宏定义,每个kernel版本都是不同的,需要用注释命令进行查看。
#define SUPER_BLOCKS_ADDRESS 0xffffffff81c72cb0// $cat /proc/kallsyms | grep super_block
#define SB_LOCK_ADDRESS 0xffffffff81fd5fa0// cat /proc/kallsyms | grep sb_lock
#define FILE_SYSTEM_ADDRESS 0xffffffff81fd6b88
#define FILE_SYSTEM_LOCK_ADDRESS 0xffffffff81fd6b80
int traverse_superblock(void)
{
struct super_block *sb;
struct list_head *pos;
struct list_head *linode;
struct inode *pinode;
// struct hlist_head *ldentry;
struct dentry *pdentry,*parents;
// char *buffer= kmalloc(sizeof(char)*10000,GFP_KERNEL);
unsigned long long count = 0;
printk("print some fields of super blocks:\n");
// if(buffer==NULL)
// return -ENOMEM;
spin_lock((spinlock_t *)SB_LOCK_ADDRESS);
list_for_each(pos,(struct list_head *)SUPER_BLOCKS_ADDRESS)
{
sb=list_entry(pos,struct super_block,s_list);
printk("dev_t: %d, %d\n",MAJOR(sb->s_dev),MINOR(sb->s_dev));
printk("fs_name: %s\n",sb->s_type->name);
list_for_each(linode,&sb->s_inodes)
{
pinode = list_entry(linode,struct inode,i_sb_list);
count++;
printk("%lu[",pinode->i_ino);
// pdentry = d_find_alias(pinode);
hlist_for_each_entry(pdentry,&pinode->i_dentry,d_alias)
{
parents = pdentry;
while (!IS_ROOT(parents))
{
printk("%s->",parents->d_name.name);
parents = parents->d_parent;
}
//memset(buffer,'\0',sizeof(buffer));
//buffer = dentry_path_raw(parents,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
//printk("%s",buffer);
}
printk("/]\n");
}
printk("\n");
}
spin_unlock((spinlock_t *)SB_LOCK_ADDRESS);
printk("the number of inodes: %llu\n",sizeof(struct inode *)*count);
}
static int print_init(void)
{
struct file_system_type **pos;
printk("\n\nprint file system_type:\n");
read_lock((rwlock_t *)FILE_SYSTEM_LOCK_ADDRESS);
pos =(struct file_system_type **)FILE_SYSTEM_ADDRESS;
while(*pos)
{
printk("name: %s\n",(*pos)->name);
pos = &((*pos)->next);
}
read_unlock((rwlock_t *)FILE_SYSTEM_LOCK_ADDRESS);
return 0;
}
static int __init traverse_init(void)
{
// print_init();
traverse_superblock();
return 0;
}
这里我们要阐述一个问题,比如我们想得到一个dentry的fullpath,需要一直向上遍历d_parent。判断是否到root path ,就是判断他是否是指向自己就可以了。
struct file_system_type **pos是一个指针数组,每个元素长度都是不同的。
dmesg.log