代理模式是一种常用的设计模式,他可以使得真实的角色就是实现业务的逻辑,不用关心非其本职责的实务,而是依靠后期代理实现。
这种方式可以实现解耦,让我们类的职责更加明确。
代理模式有很多种,有普通代理,强制代理,还有动态代理。
普通代理模式与强制代理模式的区别在于真正实现业务的逻辑由谁创建?强制代理模式表示必须由业务者创建,普通代理则认为可以由代理者创建!
这种普通代理模式主要应用在smart_ptr中。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class IGamePlayer
{
public:
virtual void login(string user,string password) =0;
virtual void killBoss()=0;
virtual void update()=0;
};
class GamePlayer:public IGamePlayer
{
private :
string name;
public:
GamePlayer(IGamePlayer *_gameplayer,string _name)
{
name = _name;
if(_gameplayer==NULL)
cout << "_gameplayer failture" << endl;
}
void killBoss(){ cout << "killBoss" <<endl;}
void login(string user,string password){ cout << user << " "<<password <<endl;}
void update(){ cout << "update!" <<endl; }
};
class GamePlayerProxy:public IGamePlayer
{
private:
IGamePlayer *gameplayer;
public:
GamePlayerProxy(string name)
{
gameplayer = new GamePlayer(this,name);
if(gameplayer ==NULL)
cout << "Create failture!" << endl;
}
void killBoss() {gameplayer->killBoss();}
void login(string user,string password){gameplayer->login(user,password);}
void update(){gameplayer->update();}
};
int main()
{
IGamePlayer *proxy = new GamePlayerProxy("user1");
proxy->login("lzz","lzz");
proxy->killBoss();
proxy->update();
delete proxy;
return 0;
}
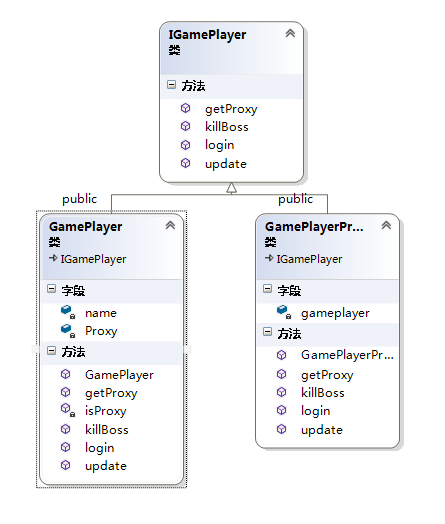
强制代理与普通代理的不同在于业务函数必须由业务类制剂创建!并由业务类返回代理者!
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class IGamePlayer
{
public:
virtual void login(string user,string password) =0;
virtual void killBoss()=0;
virtual void update()=0;
virtual IGamePlayer* getProxy()=0;
};
class GamePlayerProxy:public IGamePlayer
{
private:
IGamePlayer *gameplayer;
public:
GamePlayerProxy(IGamePlayer *_gameplayer)
{
this->gameplayer = _gameplayer;
}
void killBoss() {this->gameplayer->killBoss();}
void login(string user,string password){this->gameplayer->login(user,password);}
void update(){this->gameplayer->update();}
IGamePlayer* getProxy(){ return this;}
};
class GamePlayer:public IGamePlayer
{
private :
string name;
IGamePlayer *Proxy;
bool isProxy()
{
if(Proxy==NULL)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public:
GamePlayer(string _name)
{
name = _name;
}
IGamePlayer* getProxy()
{
this->Proxy = new GamePlayerProxy(this);
return Proxy;
}
void killBoss(){ if(isProxy())cout << "killBoss" <<endl;}
void login(string user,string password){ if(isProxy()) cout << user << " "<<password <<endl;}
void update(){ if(isProxy())cout << "update!" <<endl; }
};
int main()
{
IGamePlayer *player = new GamePlayer("user1");
IGamePlayer *proxy = player->getProxy();
proxy->login("lzz","lzz");
proxy->killBoss();
proxy->update();
delete proxy;
return 0;
}
还有一种动态代理的模式,主要用在Java中,动态代理在实现阶段不在乎代理谁,而主要在运行阶段才真正的代理。
handler只需要继承InvocationHandler即可,然后再invoke()中返回要调用的方法或者函数。