之前分析了文件系统主要的数据结构inode,dentry,super_block,file.
为了加快文件的一些操作,还引入了中间的数据结构。
struct file_system_type(include/linux/fs.h)
file_system_type结构用来描述具体的文件系统的类型信息。被Linux支持的文件系统,都有且仅有一 个file_system_type结构而不管它有零个或多个实例被安装到系统中。
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
#define FS_REQUIRES_DEV 1
#define FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA 2
#define FS_HAS_SUBTYPE 4
#define FS_USERNS_MOUNT 8 /* Can be mounted by userns root */
#define FS_USERNS_DEV_MOUNT 16 /* A userns mount does not imply MNT_NODEV */
#define FS_RENAME_DOES_D_MOVE 32768 /* FS will handle d_move() during rename() internally. */
struct dentry *(*mount) (struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *);
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;
struct file_system_type * next;
struct hlist_head fs_supers;
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key s_vfs_rename_key;
struct lock_class_key s_writers_key[SB_FREEZE_LEVELS];
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
};
和路径查找相关:
struct nameidata(include/linux/namei.h)
struct nameidata {
struct path path;
struct qstr last;
struct path root;
struct inode *inode; /* path.dentry.d_inode */
unsigned int flags;
unsigned seq, m_seq;
int last_type;
unsigned depth;
char *saved_names[MAX_NESTED_LINKS + 1];
};
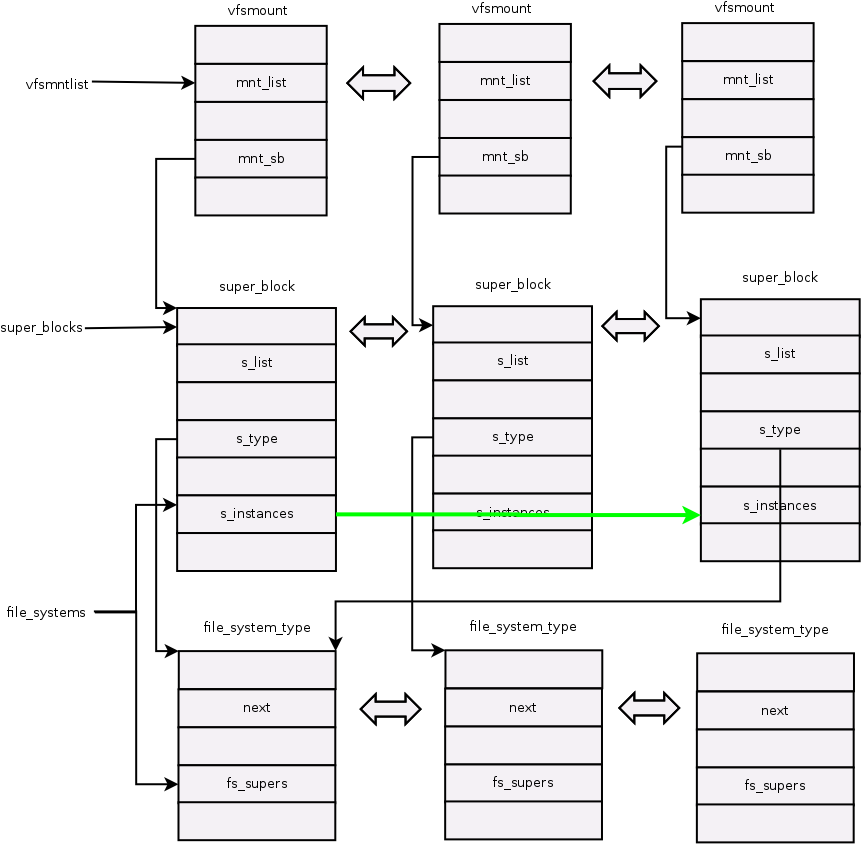
被Linux支持的文件系统,都有且仅有一个file_system_type结构而不管它有零个或多个实例被安装到系统 中。每安装一个文件系统,就对应有一个超级块和安装点。也就是说如果有多个ext4 文件系统,也就有多个ext4的super_block 与 vfsmount 。
超级块通过它的一个域s_type指向其对应的具体的文件系统类型。具体的 文件系统通过file_system_type中的一个域fs_supers链接具有同一种文件类型的超级块。同一种文件系统类型的超级块通过域s_instances链 接。
通过下图,我们可以看到第一个与第三个super_block都指向同一个file_system_type
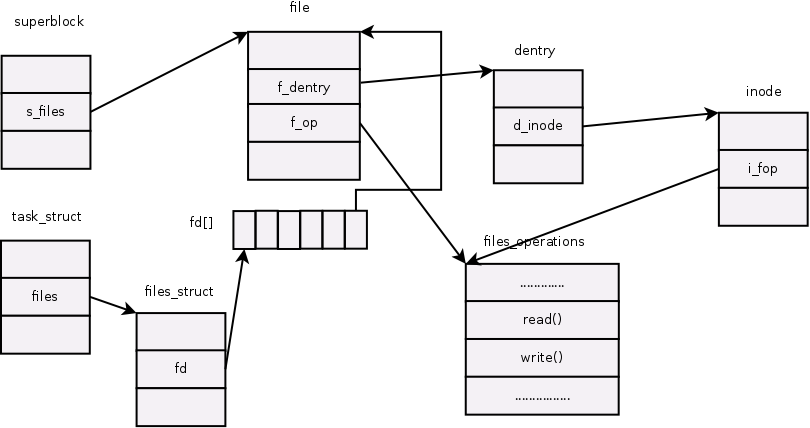
从下图可知,进程通过task_struct中的一个域files_struct files来找到它当前所打开的文件对象;而我们通常所说的文件 描述符其实是进程打开的文件对象数组的索引值。文件对象通过域f_dentry找到它对应的dentry对象,再由dentry对象的域d_inode找 到它对应的索引结点,这样就建立了文件对象与实际的物理文件的关联。
这里有一个非常重要的数据结构
struct files_struct(include/linux/fdtable.h)
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
/*
* read mostly part
*/
atomic_t count;
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
struct fdtable fdtab;
/*
* written part on a separate cache line in SMP
*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
int next_fd;
unsigned long close_on_exec_init[1];
unsigned long open_fds_init[1];
struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};
我们可以看到fd_array 这个二维fd连接一个struct file类型的数据结构,这个struct file就是连接进程与文件的媒介,比dentry,inode更加高级!
通过学习VFS文件结构,我们就可以理解跨文件系统传输的基本原理。
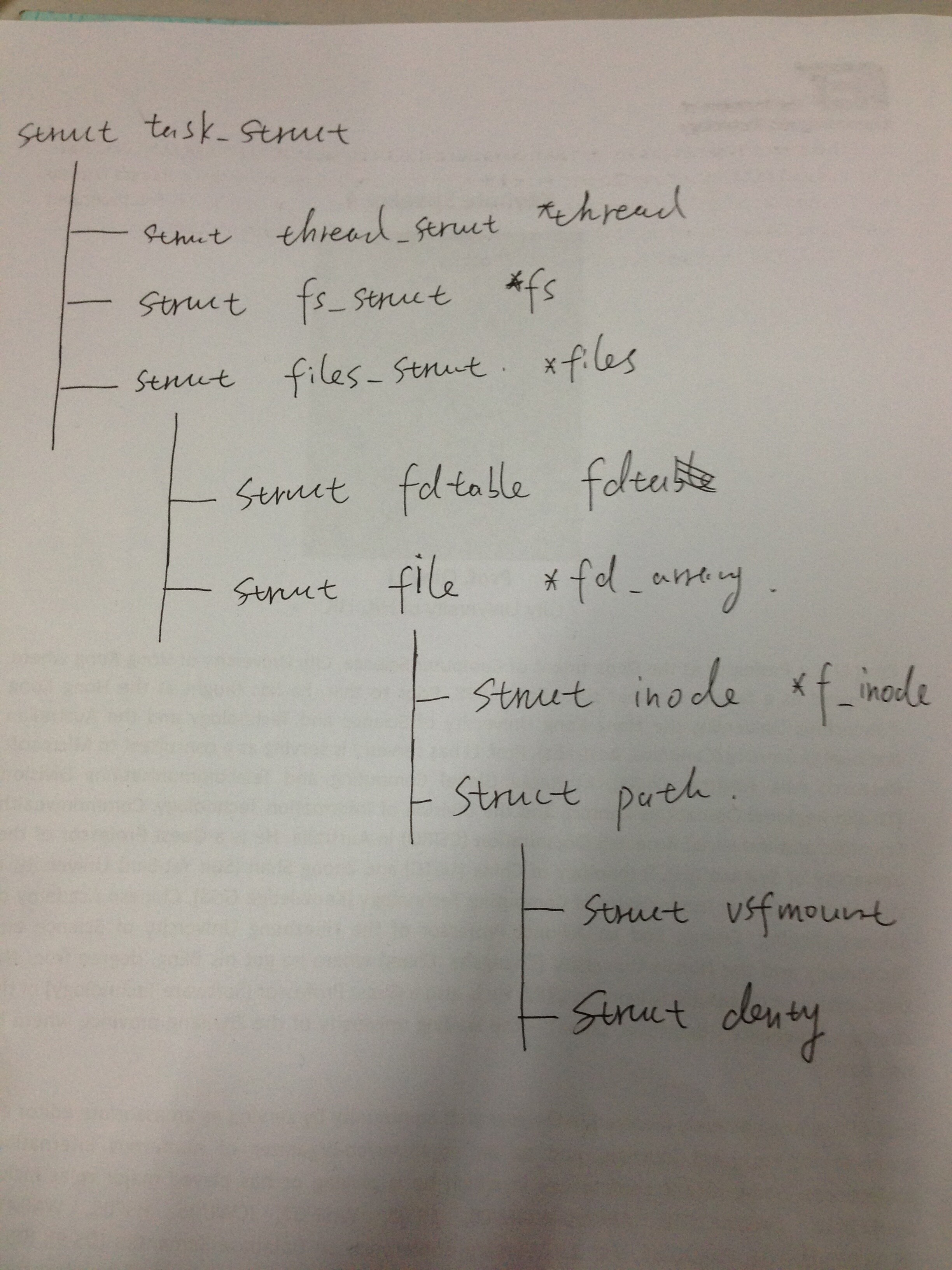
下面的图我是按照kernel 3.14.8来画的,可以清晰的看出task_struct文件结构: