之前把主要的设计模式都学了一遍,但是在实际项目中,经常是几个模式一同使用。
我找了一个使用混合模式的场景,并用C++进行实现。
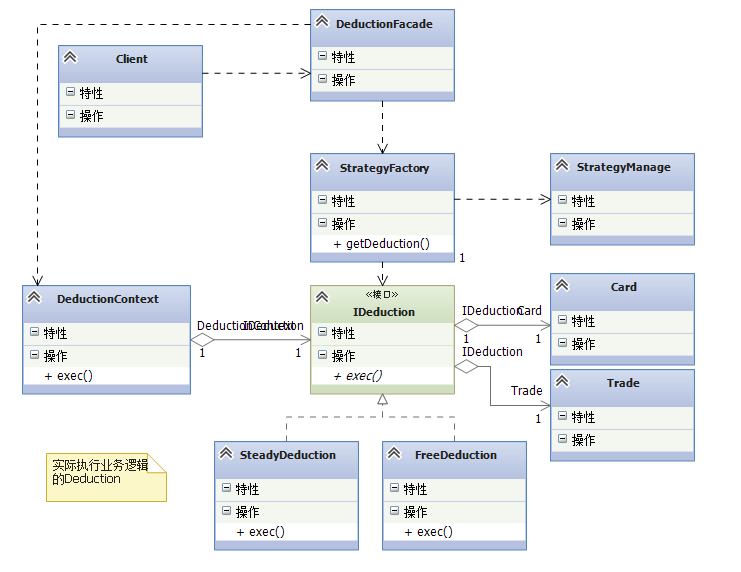
这个场景主要是使用工厂模式+策略模式+门面模式
场景:设计一个交易系统中的子模块——扣款子模块
扣款子模块中主要包括两部分:
1.IC卡类和交易信息类
其中IC卡中包括两种金额:固定金额和自由金额;交易信息类负责记录每一笔交易。
2.扣款策略类
扣款策略有以下两种:
a. IC卡固定金额 = IC卡现有固定金额-交易金额/2
IC卡自由金额 = IC卡自由金额-交易金额/2
b. 全部消费从IC卡自由金额中扣除
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Card
{
private:
string No;
int steadyMoney; //卡内固定交易金额
int freeMoney; //卡内自由交易金额
public:
string getNo() {return No;}
void setNo(string no) {No = no;}
int getSteadyMoney() {return steadyMoney;}
void setSteadyMoney(int steadyMoney) {this->steadyMoney = steadyMoney;}
int getFreeMoney() { return freeMoney; }
void setFreeMoney(int freeMoney) { this->freeMoney = freeMoney;}
};
class Trade
{
private:
string tradeNo;
int mount; //交易金额
public:
string getTradeNo() { return tradeNo; }
void setTradeNo(string tradeNo) { this->tradeNo = tradeNo; }
int getMount() {return mount;}
void setMount(int mount) { this->mount = mount;}
};
class IDeduction
{
public:
virtual bool exec(Card *card, Trade *trade) = 0;
};
class SteadyDeduction:public IDeduction
{
public:
SteadyDeduction(){}
~SteadyDeduction(){}
bool exec(Card *card, Trade *trade)
{
int halfMoney = (int)(trade->getMount() / 2.0);
card->setSteadyMoney(card->getSteadyMoney() - halfMoney);
card->setFreeMoney(card->getFreeMoney() - halfMoney);
return true;
}
};
class FreeDeduction:public IDeduction {
public :
FreeDeduction(){}
~FreeDeduction(){}
bool exec(Card *card, Trade *trade)
{
card->setFreeMoney(card->getFreeMoney() - trade->getMount());
return true;
}
};
class DeductionContext {
private:
IDeduction *deduction;
public :
DeductionContext(IDeduction *deduction) {
this->deduction = deduction;
}
bool exec(Card *card, Trade *trade) {
return this->deduction->exec(card, trade);
}
};
class StrategyManage
{
private:
string value;
public:
StrategyManage(string value) {
this->value = value;
}
string getValue() { return value;}
};
class StrategyFactory {
public :
IDeduction *deduction;
IDeduction* getDeduction(string strategy) {
try {
if(strategy=="SteadyDeduction")
deduction = new SteadyDeduction();
else if(strategy=="FreeDeduction")
deduction = new FreeDeduction();
} catch (exception e) {
}
return deduction;
}
};
//扣款模块封装
class DeductionFacade {
public:
Card *deduct(Card *card, Trade *trade) {
StrategyManage *reg = new StrategyManage("FreeDeduction"); //获得消费策略
StrategyFactory *factory = new StrategyFactory();
IDeduction *deduction = factory->getDeduction(reg->getValue()); //初始化一个消费策略 对象
DeductionContext *context = new DeductionContext(deduction); //执行封装
context->exec(card, trade); //执行扣款
return card;
}
private:
// StrategyManage getDeducationType(Trade trade) {
// if (trade.getTradeNo().contains("abc")) {
// return StrategyManage.FreeDeducation;
// }else {
// return StrategyManage.SteadyDeduction;
// }
//}
};
class Client {
public :
Card *initCard() {
Card *card = new Card();
card->setNo("10000");
card->setFreeMoney(1000);
card->setSteadyMoney(1000);
return card;
}
Trade *initTrade() {
Trade *trade = new Trade();
trade->setMount(0);
trade->setTradeNo("");
return trade;
}
Trade *CreateTrade(int charge) {
Trade *trade = new Trade();
trade->setMount(charge);
trade->setTradeNo("asasdasa");
return trade;
}
void showCard(Card *card)
{
cout<< card->getFreeMoney() << "\t"<<card->getSteadyMoney() << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Client *cli =new Client();
DeductionFacade *facade =new DeductionFacade();
Card *card = cli->initCard();
Trade *trade = cli->initTrade();
trade = cli->CreateTrade(100);
cli->showCard(card);
card = facade->deduct(card,trade);
cli->showCard(card);
return 0;
}
在该场景中用到如下几个设计模式:
策略(strategy)模式:负载对扣款策略进行封装,保证了两个策略可以自由的切换。
工厂(factory)模式:修正策略模式必须对外暴露具体策略的问题,由工厂模式直接产生一个具体策略对象,其他模块则不需要依赖具体策略。
门面(facade)模式:负责对复杂的扣款系统进行封转,封转的结果就是避免高层模块深入子系统内部,同时提供系统高内聚、低耦合的特性。